
WentWest ISIA Activity Update
Diabetes Type 2 poses a significant health challenge in Western Sydney, affecting 18% of adults attending emergency and general practice, with 30% undiagnosed prediabetes. Regular HbA1c monitoring is crucial for effective diabetes management. To address this, Western Sydney PHN applied ISIA and IHI principles to deliver Diabetes Continuous Quality Improvement (CQI) initiatives. This includes integrates training and education, CQI activities, resources and toolkits, and data-driven report to enhance primary care.
The project team collaborated with a General Practice, including GPs, practice nurses, receptionists, a pharmacist, and a non-clinical QI Champion, to establish an Aim Statement and SMART goals for improving HbA1c control in Type 2 Diabetes patients.
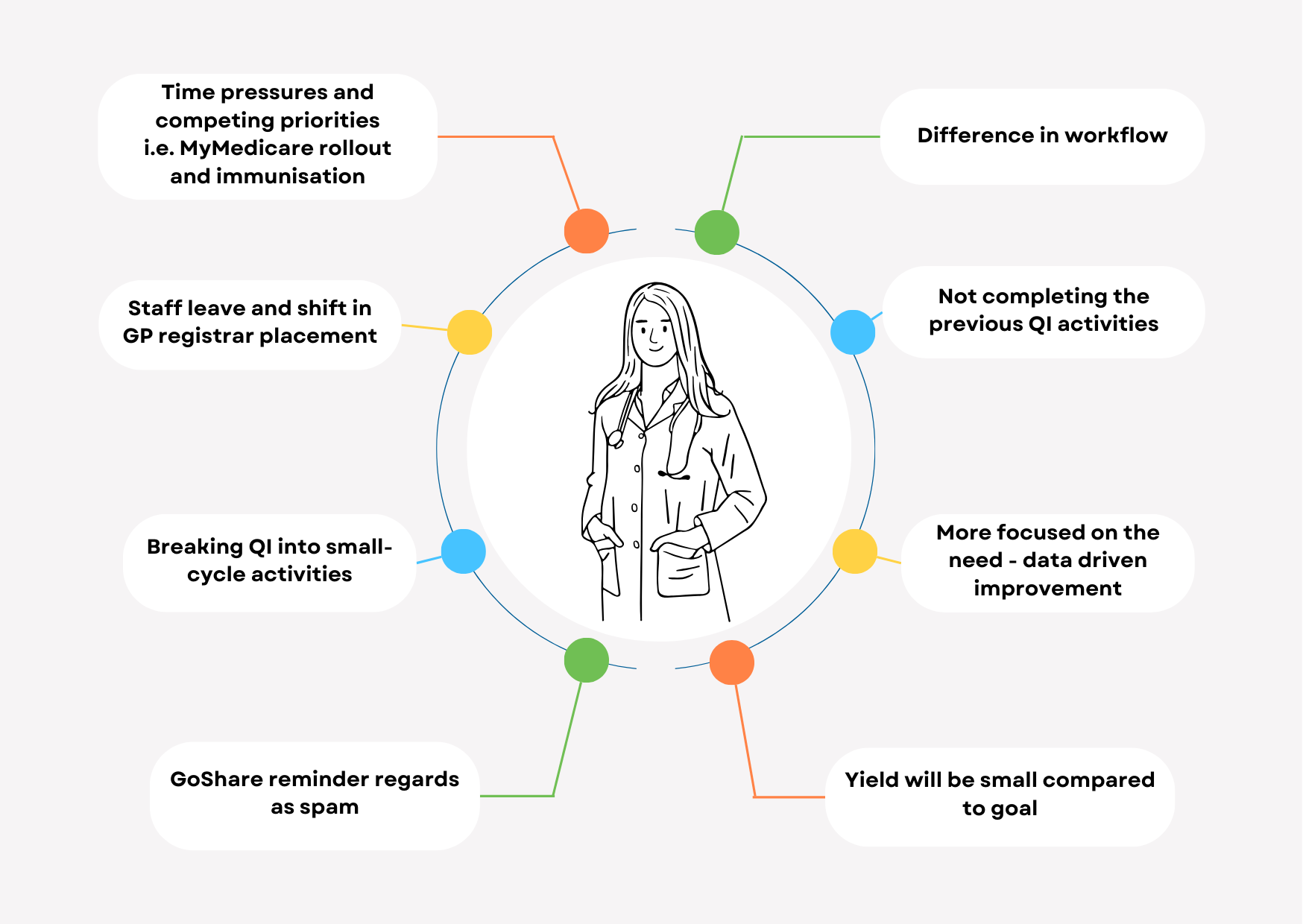
As a team when we went to the practice to implement the QI we observed the following challenges:
An initial meeting was held utilising a fishbone diagram methodology to identify challenges and barriers in conducting CQI activities and recalling patients for HbA1c tests. The identified challenges included:
How we overcame those challenges:
Using IHI tools, the team identified challenges strategies to overcome these challenges by:
- Whole team approach and team meeting
- Identifying and allocate roles and responsibility
- Streamline processes using workflows to map out current patient journey
- Fortnightly meetings with the practice to monitor progress and address barriers
- Practice Quality Improvement plan and PDSA cycle to test change and track progress
- Data-driven reports provided monthly
Change Ideas
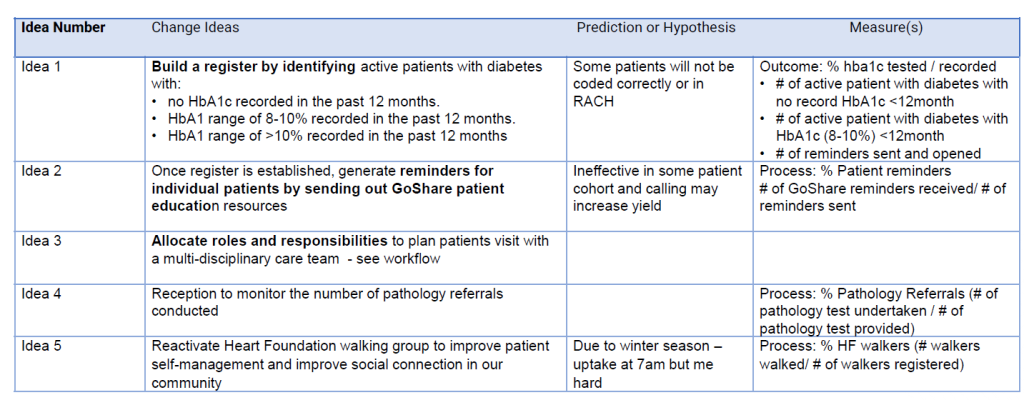
The team showed interest and were excited in the following approaches:
To implement changes, the practice drafted the Model for Improvement and PDSA cycles to test their ideas. Fortnightly practice meetings were scheduled with the practice team and PHN to monitor progress and address barriers.
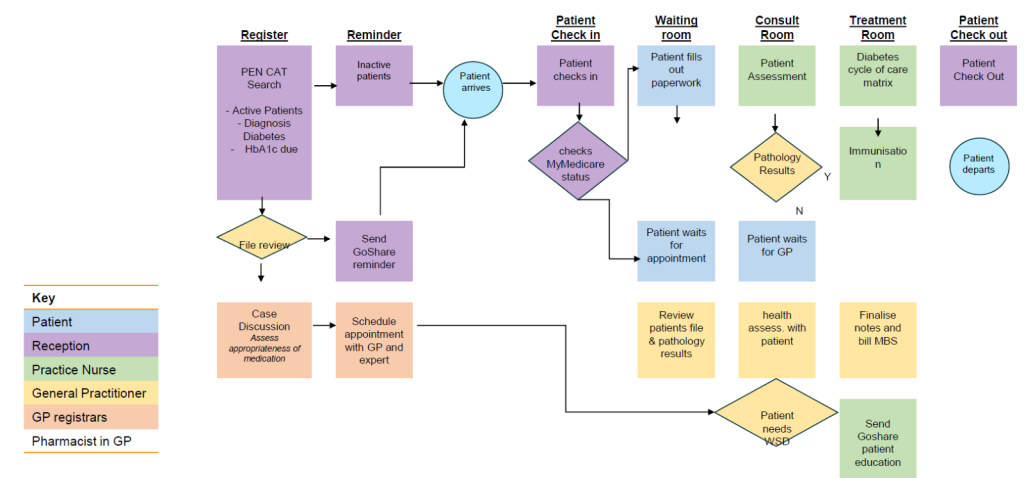
Draft current Journey Diabetes Patient HbA1c recorded in <12 months
As a PHN we had the following learnings from the ISIA project that we would like to incorporate in other QI initiatives we undertake with the general practices:
The aim is to embed continuous quality improvement focused on diabetes care in primary care, addressing key challenges and leveraging opportunities to improve outcomes for individuals living with diabetes.
